What Kind Of Message Architecture Supports All Tcp Ip Apllication Layer Protocols And Services
What is the TCP/IP Model?
TCP/IP Model helps y'all to determine how a specific computer should exist continued to the net and how data should exist transmitted betwixt them. It helps you to create a virtual network when multiple computer networks are connected together. The purpose of TCP/IP model is to let communication over large distances.
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol. TCP/IP Stack is specifically designed as a model to offer highly reliable and cease-to-stop byte stream over an unreliable internetwork.
In this TCP/IP tutorial, you volition learn:
- TCP Characteristics
- Four Layers of TCP/IP model
- Awarding Layer
- Transport Layer
- Net Layer
- The Network Interface Layer
- Differences between OSI and TCP/IP models
- Most Mutual TCP/IP Protocols
- Advantages of the TCP/IP model
- Disadvantages of the TCP/IP model
TCP Characteristics
Here, are the essential characteristics of TCP IP protocol:
- Support for a flexible TCP/IP architecture
- Adding more than system to a network is easy.
- In TCP IP protocols suite, the network remains intact until the source, and destination machines were functioning properly.
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol.
- TCP offers reliability and ensures that data which arrives out of sequence should put back into order.
- TCP allows yous to implement menses control, so sender never overpowers a receiver with data.
Four Layers of TCP/IP model
In this TCP/IP tutorial, we will explain different layers and their functionalities in TCP/IP model:
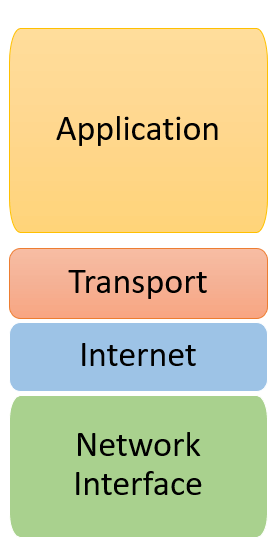
The functionality of the TCP IP model is divided into four layers, and each includes specific protocols.
TCP/IP is a layered server architecture system in which each layer is divers according to a specific function to perform. All these four TCP IP layers work collaboratively to transmit the information from one layer to another.
- Application Layer
- Send Layer
- Internet Layer
- Network Interface
Four Layers of TCP/IP model
Awarding Layer
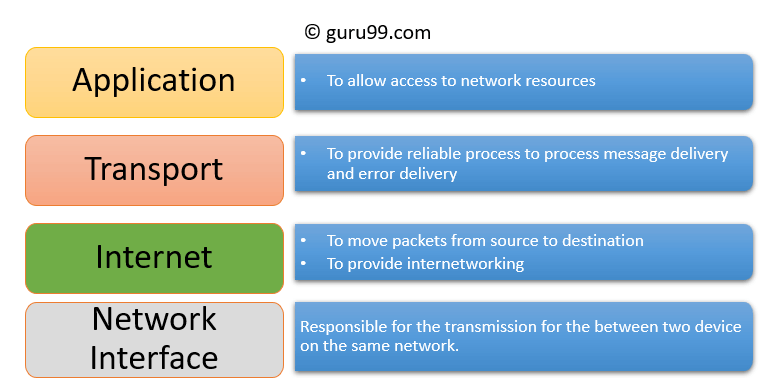
Application layer interacts with an application program, which is the highest level of OSI model. The application layer is the OSI layer, which is closest to the cease-user. Information technology ways the OSI application layer allows users to interact with other software application.
Application layer interacts with software applications to implement a communicating component. The interpretation of information by the application program is always outside the scope of the OSI model.
Instance of the application layer is an awarding such equally file transfer, e-mail, remote login, etc.
The function of the Awarding Layers are:
- Application-layer helps y'all to identify communication partners, determining resources availability, and synchronizing communication.
- It allows users to log on to a remote host
- This layer provides diverse e-mail services
- This application offers distributed database sources and access for global information about diverse objects and services.
Send Layer
Transport layer builds on the network layer in order to provide data ship from a procedure on a source organization machine to a process on a destination system. It is hosted using single or multiple networks, and too maintains the quality of service functions.
It determines how much data should be sent where and at what charge per unit. This layer builds on the message which are received from the application layer. Information technology helps ensure that information units are delivered error-costless and in sequence.
Send layer helps you to control the reliability of a link through menses control, error command, and partitioning or de-sectionalisation.
The transport layer as well offers an acknowledgment of the successful data manual and sends the next data in case no errors occurred. TCP is the best-known example of the transport layer.
Important functions of Send Layers:
- It divides the message received from the session layer into segments and numbers them to make a sequence.
- Transport layer makes sure that the message is delivered to the correct process on the destination machine.
- It also makes sure that the entire bulletin arrives without whatsoever fault else it should be retransmitted.
Internet Layer
An internet layer is a second layer of TCP/IP layes of the TCP/IP model. It is also known as a network layer. The main work of this layer is to send the packets from any network, and any computer withal they reach the destination irrespective of the road they have.
The Internet layer offers the functional and procedural method for transferring variable length data sequences from one node to some other with the help of various networks.
Message delivery at the network layer does not give whatever guaranteed to be reliable network layer protocol.
Layer-direction protocols that belong to the network layer are:
- Routing protocols
- Multicast group management
- Network-layer address consignment.
The Network Interface Layer
Network Interface Layer is this layer of the four-layer TCP/IP model. This layer is also called a network admission layer. It helps you to defines details of how data should be sent using the network.
Information technology also includes how $.25 should optically be signaled by hardware devices which direct interfaces with a network medium, similar coaxial, optical, coaxial, fiber, or twisted-pair cables.
A network layer is a combination of the data line and defined in the commodity of OSI reference model. This layer defines how the data should be sent physically through the network. This layer is responsible for the manual of the data between two devices on the same network.
Differences between OSI and TCP/IP models

Difference between OSI and TCP/IP model
Here, are some of import differences betwixt the OSI and TCP/IP model:
| OSI Model | TCP/IP model |
|---|---|
| It is developed past ISO (International Standard Arrangement) | It is developed by ARPANET (Advanced Inquiry Project Agency Network). |
| OSI model provides a clear distinction betwixt interfaces, services, and protocols. | TCP/IP doesn't have whatsoever articulate distinguishing points between services, interfaces, and protocols. |
| OSI refers to Open up Systems Interconnection. | TCP refers to Transmission Control Protocol. |
| OSI uses the network layer to define routing standards and protocols. | TCP/IP uses only the Internet layer. |
| OSI follows a vertical arroyo. | TCP/IP follows a horizontal approach. |
| OSI model apply two carve up layers physical and data link to define the functionality of the bottom layers. | TCP/IP uses only i layer (link). |
| OSI layers have vii layers. | TCP/IP has four layers. |
| OSI model, the ship layer is only connection-oriented. | A layer of the TCP/IP model is both connexion-oriented and connectionless. |
| In the OSI model, the information link layer and concrete are carve up layers. | In TCP, physical and data link are both combined as a single host-to-network layer. |
| Session and presentation layers are not a part of the TCP model. | There is no session and presentation layer in TCP model. |
| It is defined after the appearance of the Internet. | It is defined before the advent of the internet. |
| The minimum size of the OSI header is 5 bytes. | Minimum header size is 20 bytes. |
Most Common TCP/IP Protocols
Some widely used nigh mutual TCP/IP protocol are:
TCP:
Transmission Control Protocol is an internet protocol suite which breaks upwardly the message into TCP Segments and reassembling them at the receiving side.
IP:
An Net Protocol address that is as well known as an IP address is a numerical label. Information technology is assigned to each device that is connected to a calculator network which uses the IP for communication. Its routing function allows internetworking and substantially establishes the Internet. Combination of IP with a TCP allows developing a virtual connexion between a destination and a source.
HTTP:
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a foundation of the World Wide Web. It is used for transferring webpages and other such resource from the HTTP server or web server to the spider web client or the HTTP client. Whenever you utilise a web browser similar Google Chrome or Firefox, you lot are using a web client. It helps HTTP to transfer web pages that you lot request from the remote servers.
SMTP:
SMTP stands for Simple mail transfer protocol. This protocol supports the e-mail is known every bit a simple mail transfer protocol. This protocol helps yous to send the data to another email address.
SNMP:
SNMP stands for Elementary Network Direction Protocol. It is a framework which is used for managing the devices on the cyberspace past using the TCP/IP protocol.
DNS:
DNS stands for Domain Name Arrangement. An IP address that is used to identify the connection of a host to the net uniquely. All the same, users prefer to apply names instead of addresses for that DNS.
TELNET:
TELNET stands for Terminal Network. It establishes the connexion between the local and remote estimator. It established connexion in such a manner that yous can simulate your local system at the remote system.
FTP:
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. Information technology is a by and large used standard protocol for transmitting the files from ane auto to some other.
Advantages of the TCP/IP model
Here, are pros/benefits of using the TCP/IP model:
- It helps y'all to constitute/set a connection between different types of computers.
- It operates independently of the operating organisation.
- It supports many routing-protocols.
- It enables the internetworking between the organizations.
- TCP/IP model has a highly scalable client-server architecture.
- Information technology tin be operated independently.
- Supports a number of routing protocols.
- Information technology tin can be used to found a connection between two computers.
Disadvantages of the TCP/IP model
Here, are few drawbacks of using the TCP/IP model:
- TCP/IP is a complicated model to prepare and manage.
- The shallow/overhead of TCP/IP is college-than IPX (Internetwork Packet Substitution).
- In this, model the send layer does not guarantee delivery of packets.
- Replacing protocol in TCP/IP is not easy.
- Information technology has no clear separation from its services, interfaces, and protocols.
Summary:
- The full form of TCP/IP model explained every bit Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol.
- TCP supports flexible architecture
- Awarding layer interacts with an application plan, which is the highest level of OSI model.
- Internet layer is a 2d layer of the TCP/IP model. It is also known as a network layer.
- Transport layer builds on the network layer in guild to provide information transport from a process on a source arrangement machine to a process on a destination system.
- Network Interface Layer is this layer of the 4-layer TCP/IP model. This layer is also called a network access layer.
- OSI model is developed by ISO (International Standard Organization) whereas TCP/IP model is developed past ARPANET (Advanced Inquiry Project Agency Network).
- An Internet Protocol address that is too known as an IP address is a numerical label.
- HTTP is a foundation of the World wide web.
- SMTP stands for Unproblematic mail transfer protocol which supports the due east-mail is known as a simple mail transfer
- SNMP stands for Uncomplicated Network Management Protocol.
- DNS stands for Domain Name System.
- TELNET stands for Terminal Network. It establishes the connection between the local and remote calculator
- FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. It is a mostly used standard protocol for transmitting the files from one machine to another.
- The biggest do good of TCP/IP model is that it helps you to establish/set upwards a connection between dissimilar types of computers.
- TCP/IP is a complicated model to set upwardly and manage.
- What are the different types of TCP/IP layers?
There are iv types of TCP/IP layers.- Awarding layer
- Transport layer
- Cyberspace layer
- Network interface
What Kind Of Message Architecture Supports All Tcp Ip Apllication Layer Protocols And Services,
Source: https://www.guru99.com/tcp-ip-model.html
Posted by: cameronlacent.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Kind Of Message Architecture Supports All Tcp Ip Apllication Layer Protocols And Services"
Post a Comment